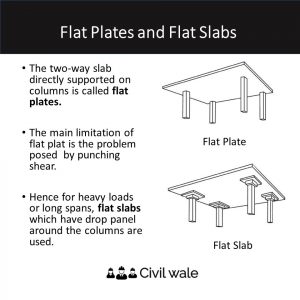
In traditional construction methods are based on the principle that the slab is supported by beams and the beams are supported by columns. In the flat slab system, beams are avoided and the slab is directly supported in columns. Sometimes drop panels are used above the columns to support the flat slabs.
Flat slab is an effective choice for asymmetrical construction of column layouts, providing good aesthetic appearance, flexible for interior design and easy to make different kinds of floor layouts.
Types of Flat Slabs
- Flat plate
- Flat slab with drop panel
- Flat slab with a column head
- Flat slab with column head and drop panel
Drop panels and column heads are used above the column to give support and increase the shear strength of the slab. Also, reduce the deflection in the slab when it comes to contact with the column. The drop panels also reduce the steel requirements for negative moments at column supports. Drop panels are rectangle in shape and length not less than one-third of the panel length in that direction. The column head is primarily used to increase the strength of the slab to resist punching shear.
The thickness of the slab varies from 125mm to 300mm for a span of 4 to 9 meters. Thin slab design helps to provide increased floor height. To maintain structural stability extra reinforcements are required in slab design.
Failures in Flat slabs
Punching shear failure is one of the main issue facing while flat slab design. It is the failure of the flat slab (Reinforced concrete slab) when subjected to high localized stress. It happens around the column support region or the region where the column comes to contact with the slab.
The phenomenon behind the punching shear failure is the concentrated support reaction from the column creates a pushing effect on the slabs and due to the loads on the slabs cracks generates abound the loaded areas of the slab which results in conical failure of slab. To solve this problem the following methods are adopted:
- Increase overall slab thickness
- Providing drop panels and Column heads
- Increase the size of column size enough to cover up the shear perimeter
- Providing good shear reinforcement
Advantages of Flat Slab
- Construction time can be reduced, because of the absence of beams creates the making of formwork a lot easier and that makes construction economic to some extent
- Reduction in floor height can be achieved
- Implementation of flat slabs makes the rooms or hall very flexible for interior designing and it gives an attractive pleasant appearance in buildings, also creates good acoustics performance
- Flats slabs can reduce a considerable amount of dead load and it is beneficial for columns and foundations
- Easy to install sprinkler and pipes across the ceiling.
Disadvantages of Flat Slab
- The slab column connection is not up to the mark the case of rigidity compared to column beam connection
- Risks of punching shear failure are high due to the high shear load concentration around the column
- The performance of flat slab under temperature loading is poor
- The structural efficiency is less under earthquake loading and lateral loads (lateral stiffness are relatively less)
Also Read:



This article is very useful and amazing. Plz write more . Thank u
hello Dear ,
you are working is so very interesting about posting concerning Flat slab and other civil-engineering .really i got many new concepts about flat slab so pleas email to me if you have any full analysis in designing building with flat slab.
Regards,