The building bye-laws or building codes are defined as the standards and norms set by the government authorities to ensure the health and comfort of users, to safeguard the workers during construction; and to provide enough safety to the public in general.
Read More: Building Code: An Impeccable Guide to Civil Engineers
An order prescribed is known as the regulation while the law of a local authority is known as bye-law.
The Objective of Building Bye-laws:
- To provide guidelines to the designing architects and engineers. It becomes easier to pre-plan building provisions and activities.
- The building bye-laws prevent unplanned development.
- It provides safety to human beings who work and live in them against fire, noise, health hazard and structural failure.
The bye-laws and regulations govern the following building aspects:
Set-back or Building line:
The frontage margin or open space in front of the abutting road is called as set-back or building line. Beyond this line, nothing can be constructed towards the plot boundaries.
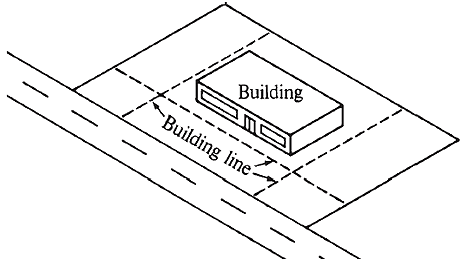
The Need for Building line:
- If absolutely necessary, the land contained in set-back may be acquired for the purpose of widening of the road.
- The setback at corner improves visibility and impart safety to the moving traffic.
- The space of setback can be used as a parking place or for developing a garden.
- It provides protection of buildings from street disturbances.
- It reduces the danger of fire by increasing the distance between the opposite buildings.
Floor Space Index or Floor area ratio:
The ratio of the total floor area inclusive of all the floors to the area on which the building stands in known as the floor space index or floor area ratio. It controls the development activity on the plot. It can be used as a measure to check the density of the population.
Floor area ratio = ( Gross Floor Area) /(Area of the plot)
For example, if the total floor area of a building across two floors is 300 sq m and the plot area is 200 sq m,
FAR = 300/200 = 1.5
Built-up area or Covered area:
The plot area minus the area due for open spaces is known as the built-up area. Following are the limitations of the built-up area mentioned in the National Building Code.
| No. | Plot Area | Maximum permissible built-up area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Less than 200 sq m | 60% with two-storeyed structure |
| 2 | 200-500 sq m | 50 % of the plot area |
| 3 | 500-1000 sq m | 40 % of the plot area |
| 4 | more than 1000 sq m | 33.33 % of the plot area |
Size of rooms:
Considering the health and proper ventilation, NBC has fixed a certain minimum area for individual rooms and apartments as below:
| S. No. | Type of Room | Minimum area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | One habitable room | 9.5 sq m width 2.4 m |
| 2 | Two habitable room | Minimum area of one room 9.5 sq m and of other 7.5 sq m width 2.4 m |
| 3 | Kitchen only | 4.5 sq m width 1.8 m |
| 4 | kitchen with store room | 5.5 sq m width of kitchen 1.8 m |
| 5 | Kitchen cum dining room | 9.5 sq m, minimum width 2.4 m |
| 6 | Bathroom | 1.8 sq m or minimum size 1.5 m x 1.2 m |
| 7 | Water Closet (w.c.) | 1.1 sq m |
| 8 | Bath WC combined | 2.8 sq m, minimum width 1.2 m |
Hight of rooms and Buildings:
As per NBC, the general criteria to determine the height of a building is 1.5 times the width of the street to which the building abuts on its front side.
- For street width of 8-12 m, the building height should not be more than 12 m
- For street width more than 12 m, the height of a building should not be more than the width of the street and in case more than 24 m.
Lighting and ventilation of Rooms:
For sufficient lighting and ventilation of rooms of buildings, opening like windows and ventilators or direct opening should be provided.
- The area of such openings excluding the area of doors should be minimum 1/10th of the floor area for dry and ho climate and minimum 1/6th of the area for wet hot climate.
- The aggregate area of doors and windows should not be less than 1/7th of the floor area of the room.
Note: Foor area means built-up area excluding areas of walls.
Water supply and sanitary positions:
Certain minimum water supply and sanitation convenience like water taps, sink, water closets washbasins etc. shall be provided as per NBC for different types of buildings.
Structural Designs (Size and section):
Each structure should be designed for safe loads, earthquake resistance, bearing capacities etc. as per relevant IS codes and NBC.
Some general thumb rule for structural design:
- Depth of foundation: 0.75 m to 1.0 m for single-storeyed building below ground level and 1.0 m to 1.3 m for two-storeyed building.
- Width of the foundation of the wall: Double the thickness of the wall just above the plinth and then add 30 cm to it will give the width of the foundation.
- Concrete in Foundation of the wall: It should be nearly equal to 5/6th the thickness of wall above the plinth.

