Concrete is a heterogeneous and composite mass, which is a mixture of cement, fine aggregates, coarse aggregates and a certain amount of water.
As the technology upgraded, it soon comes into light that standard conventional concrete, which is used in all Concreting aspects, have several drawbacks. Some of the defects may include, its low tensile strength, very heavy self-weight of concrete, delay in hardening due to the absence of suitable atmospheric conditions, freezing & thawing in cold weather, shrinkage & bleeding due to the porous behaviour of concrete, and many more.
So efforts are made with the help of technology, to strengthen the ordinary conventional concrete in all aspect, and to advance the concrete construction of the world, which will be able to reach a new high.
These efforts resulted in the invention of different types of Concretes to meet our requirements. This may be called as the upgraded version of conventional concrete.
Types of Concrete
Light Weight Concrete

One of the major disadvantages of ordinary conventional concrete is that it’s very high self-weight, which is to the extent of 2300-2500 kg/cubic metre. So efforts were made, to reduce the self-weight of concrete.
Lightweight Concrete, as the name represents, offers a very lightweight concrete which is to the extent of 800-1300 kg/cubic metre.
The lightweight property of concrete can be brought by three methods, which are as follows –
- By using Lightweight aggregates
- By omitting the sand fraction from the aggregate (known as no-fines concrete)
- By using air bubbles into the mortar (known as Aerated Concrete or Foam Concrete)
The most commonly adopted method is by using the lightweight aggregates in the place of usual mineral aggregates. Some of the lightweight aggregates are Pumice, Diatomite, Scoria, Volcanic dust, Cinders, Rice husk etc.
Advantages of Lightweight Concrete:
- The main important advantage of low weight concrete is its low density, which helps in the reduction of dead loads, and respectively increases the progress of the building, lowering handling and haulage costs.
- Low thermal conductivity is another advantage of low weight concrete, which can be attained with decreasing density.
- Low weight concrete is to be used in the place of weak soils and tall structures, for which if the floors and walls cast with low weight concrete, it results in the considerable economy.
Heavy Weight Concrete
This type of concrete is also known as High-Density Concrete. As previously mentioned low weight concrete offers a low weight than that of standard conventional concrete. Similar to that, the weight of High-Density Concrete is much higher than that of the standard conventional concrete. The weight of High-Density Concrete is to the extent of 3360-3840 kg/cubic metre, which can be increased to the extent of 5280 kg/cubic metre with the addition of iron as both in fine as well as in Coarse aggregates.
Advantages of High Weight Concrete:
- High-density concrete is mostly used in the construction of Radiation shields. As the nuclear energy industry offers a large scale production of penetrating radiation and radioactive materials, as a result of different nuclear reactors, particles accelerators, etc, concrete of very heavy density is necessary for the protection of the personnel involved in such sectors, from different biological hazards. Heavyweight concrete satisfactorily serves the purpose.
- High modulus of elasticity, low thermal expansion is another advantage of using high-density concrete.
Fibre Reinforced Concrete
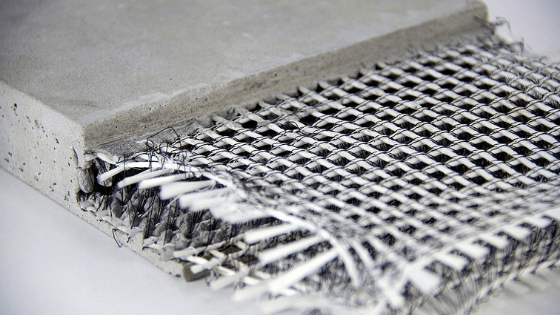
Standard Conventional concrete possesses a very low tensile strength, limited ductility and little resistance to cracking. Internal microcracks are inherently present in the concrete, and its poor tensile strength is due to the propagation of such microcracks, eventually leading to the brittle fracture of concrete.
So an attempt has been made to increase the inherent tensile strength of the concrete and to impart improvement in tensile properties of concrete. Experiments showed that the addition of closely spaced, uniformly dispersed fibres in concrete would act as a crack arrester and would substantially improve the tensile properties of concrete. This type of concrete is termed as Fibre Reinforced Concrete.
Examples of some fibres, which can be used in the production of Fibre Reinforced Concrete, are Steel fibres, polypropylene, nylon, asbestos, coral, glass & carbon. Mostly used fibre being used is steel fibre. These can be found or flat in shape, whose diameter generally varies from 0.25 to 0.75mm.
Advantages of Fibre Reinforced Concrete:
- Fibre Reinforced Concrete is extensively used in Bridge decks, artificial pavements, roads etc where the high tensile strength of concrete is of prime importance.
- Increase of tensile strength affects several other important factors of concrete considerably, which can also be used in different atmospheric condition.
White Concrete:
As already mentioned earlier, concrete is a homogeneous mixture of Cement, fine & coarse aggregates, and water, within which Cement holds the prime importance as this the material which drives the properties of the concrete to be imparted. In the manufacture of Standard Conventional Concrete, grey Portland cement is being used. When the white Portland cement is used in the place of grey Portland cement, the manufactured concrete is termed as White Cement Concrete.
White Portland Cement is very much costly and expensive, as compared to ordinary grey Portland cement, due to the some of the following reasons:
- The energy consumption of white Portland cement is about 40% higher than that of the ordinary Portland cement.
- A large amount of Iron & manganese is imparted in the manufacturing process to increase the whiteness of the cement, resulting in the cement to be more expensive in nature. So these additional materials increase the cost.
- Special precautions to be taken, while manufacturing the white cement, which respectively, increases the overall manufacturing cost of the cement.
The cost of white cement is about 4 times higher than that of an ordinary Portland cement, and the compressive strength of white cement is lower than that of OPC
Advantages of White Concrete:
- One of the most important advantages white concrete offers is that its pleasant looks from the architectural & aesthetic viewpoint, which is why it is widely being used in modern decorative works, interior as well as exterior surfaces, because of its whiteness.
- White concrete provides a neat and smooth surface owning to the higher fineness of grinding of white cement. Because of this, white concrete is mostly used for the manufacture of precast members.
Polymer Concrete
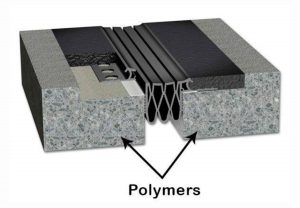
It has already been found that the concrete is porous. The porosity is due to the presence of air voids, water voids, and due to the inherent porosity of gel itself. Reduction of porosity results in considerable improvement of strength of concrete.
So efforts have been made to bring down the porous behaviour of concrete. Vibration, pressure application spinning are some of the methods which can be useful to some extents, but none of them helps to reduce the water voids and inherent porosity of gel, which is estimated to be about 28%. Experiments showed that the implementation of monomer in concrete and polymerisation satisfactorily serves to bring down the water voids in concrete. These type of concrete is known as Polymer concrete.
There are generally four types of polymer concrete being utilised:
- Polymer Impregnated Concrete(PIC)
- Polymer Cement Concrete (PCC)
- Polymer Concrete(PC)
- Partially impregnated surface coated polymer concrete
Advantages of Polymer Concrete:
- The main advantages of polymer concrete are that it provides a zero amount of water voids, which can be attributed to the increased strength of concrete.
- Polymer concrete has high toughness and very high tensile strength.
Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt concrete is a composite material, which is composed of mineral aggregates adhered with a binder. In this case, the binder often used, is Asphalt or bitumen, so the manufactured concrete is termed as Asphalt Concrete.
Asphalt concrete is widely adopted particularly for pavement construction, from the beginning of the twentieth century. The process of pavement construction by Asphalt concrete includes placing of mineral aggregates in layers, bound together with a binder, which is then compacted and rolled to obtain the desired surface.
Asphalt concrete can be broadly divided into five categories, depending upon the process of manufacturing, and binder used. These are:
- Hot-mix Asphalt concrete: It is obtained by heating the asphalt binder, and drying the aggregates before mixing. Hot-mix Asphalt concrete is used in high traffic pavements such as major highways, airfield pavements, racetracks etc.
- Warm-mix asphalt concrete: It is obtained by adding perlite waxes, or water, to the asphalt binder, before mixing. Manufacturing of these concrete requires significantly lower temperature & lower energy consumption than that of Hot-mix Asphalt concrete.
- Cold-mix Asphalt concrete: It is manufactured by emulsifying the Asphalt binder with an emulsifying agent before mixing with aggregates. This type of concrete is generally used for patchwork and on lesser trafficked service roads.
- Cutback Asphalt concrete: It is obtained by dissolving the binder in kerosene or petroleum or other volatile organic compounds.
- Mastic Asphalt: It Is produced by heating the hard grade bitumen in a cooker until it becomes a viscous liquid, after which the aggregates mix is then added.
Advantages of Asphalt Concrete
- Use of Asphalt concrete considerably lowers the emission of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases and other pollutants, which in return, results in an economical and pollution-free pavement construction.
- Pavements constructed with Asphalt concrete offers a very high skid resistance, which is why Asphalt concrete is widely adopted for the construction of high traffic roadways and racetracks.
Cold weather concrete
Standard conventional concrete which is adopted in fair weather, can not be valid for the places where temperatures prevail below 0°C. Cold weather concrete is particularly used for these purposes where the temperature is below freezing point.
Advantages of Cold Weather Concrete:
- Standard conventional concrete, when used below freezing temperatures, affects the setting and hardening process to a great extent. In case of cold weather concrete, temperatures do not pose a threat.
- The durability of concrete under this condition can be fairly much as compared to the standard conventional concrete.
Hot weather concrete
As the name indicates, this type of concrete is particularly suitable for hot atmospheric regions(generally in regions where temperatures prevail is greater than 40°C)
Advantages of Hot weather Concrete:
- Standard conventional concrete, when used in a hot region, poses a threat of bleeding and shrinkage, also due to the high temperature, the water within the concrete gets hydrated much faster than fairly atmospheric conditions, so as a result, cracks appear. Hot weather concrete prevents the quick hydration of concrete so that it can attain stipulated prescribed strength.
- It can be used in the construction of airfield pavements, and different wearing surfaces exposed to the sun.
High-Performance Concrete
As the name indicates it provides High tensile strength, greater resistance to chemical attack and very low permeability.
Shotcrete
Shotcrete is the concrete when pneumatically applied through a pressure application machines in high velocity. Nowadays Shotcrete Is widely used in the repairing purpose.
Bacterial Concrete
Can be attained with the implementation of Bacterial microorganisms. This is also called as Self-healing Concrete
Geopolymer Concrete
This type of concrete is being used where the low emission of Carbon dioxide is of prime importance.
Also Read:


very good and informative post sir
Pingback: What Is Bond Breaker | Purpose of Providing Bond Breaker | What Is Concrete Bond Breaker | What is Bond Breaker Tape