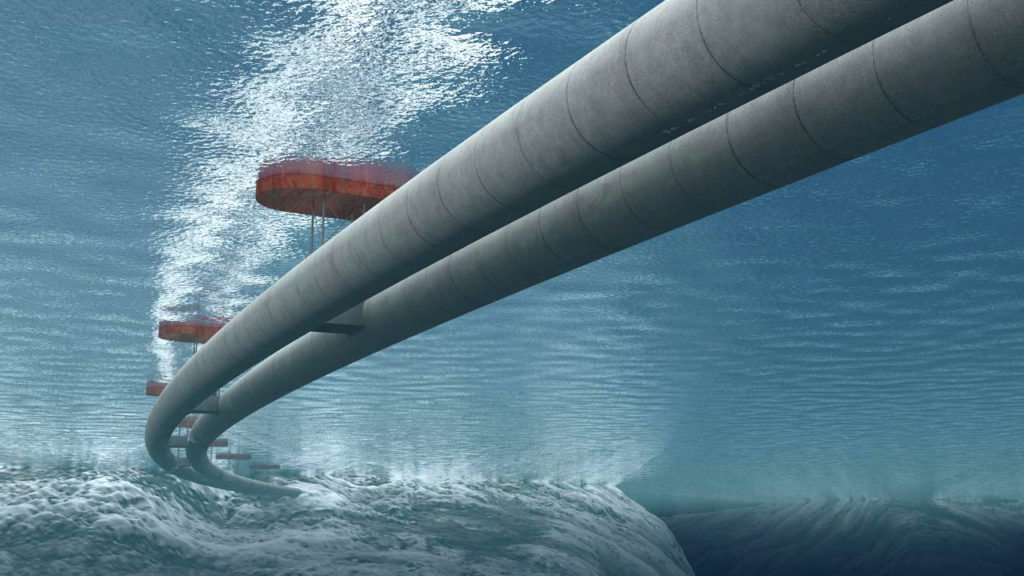
The Submerged floating Tunnel is a tube-like structure made of steel and concrete deploying the law of buoyancy to support the structure at a moderate and convenient depth. The submerged floating tunnel is an unconventional concept for crossing waterways.
An SFT is considered when the depth of the sea ocean is too deep so that no tunnel could sustain the pressure acting on it at such a level. It supported by cables anchored to the earth or by pontoons floating on the surface.
The Basic Principle of Submerged Floating Tunnel
A submerged floating tunnel is a light structure that moves in the water. The relation between buoyancy and self-weight controls the static behaviour of the tunnel and the response of dynamic forces.
The two ways in which SFT can be floated is positive and negative buoyancy.
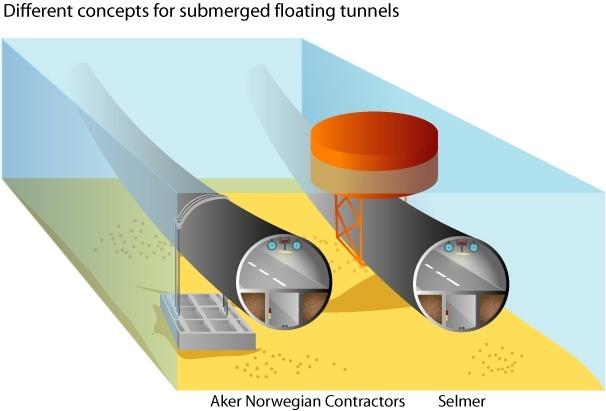
Positive buoyancy: In positive buoyancy, the submerged floating tunnel is fixed in its position by anchoring either by means of tension leg to the bottom or by means of coracle on the surface. In this, the SFT is 30 meters below the water surface
Negative buoyancy: In case of negative buoyancy, the foundation would be piers or column to sea lake. SFT is threatened to all environmental action typically in the water environment, wave current, earthquake. It should be designed to withstand all actions.
Components of Submerged Floating Tunnels (SFT):
Typically an SFT consists of the following:
- The tunnel tube for the road or railway traffic
- Tethers, vertical or inclined fixing the tube to the sea-bed
- Pontoons mounted on top of the tunnel and “anchoring”
- Gravity anchors on the sea-bed providing support for the tethers
- Shore connections at the ends of the tunnel
Features of Submerged Floating Tunnel (SFT)
- The Length of the submerged floating tunnel structure is the only distance between shores.
- SFT help in crossing lakes and other areas. lakes of special beauty or perhaps historical value will be preserved with the help of SFT
- An SFT crossing has a gentle gradient or being nearly horizontal giving considerable savings in energy used by traffic.
- It is possible to arrange parking places or service areas underground and provide a path to the surface through lifts directly into cities or recreational areas.
- An SFT is positioned at any depth below the surface arrangements so that the SFT surfaces at or very near the shoreline. This will be a benefit for connections to new or existing road systems and gives the planners the freedom to locate connections in a very flexible.
- It can be constructed away from the densely populated areas.
Challenges to be Faced
- The action of wave and current exerting on SFT produces fluid-solid coupling vibration on structure or components. The behaviour and mechanism of SFT are very complex under such actions. Construction of SFT involves a lot of material and Machinery, which causes a high amount of cost. It is difficult to save people if the fire will breakout.
- In the case of the collision of two trains, it is difficult to rescue people. It is also difficult to stop the train travelling at such high speed
- During construction and operation, one should know about many risks and uncertain factors that exist. How to identify and mitigate these risks and uncertainties.
References: